Protein is one of the essential nutrients for the human body. It is involved in various physiological functions of the body, such as building and repairing tissues, maintaining the immune system, synthesizing enzymes and hormones, etc. In our daily diet, we can get protein from both plant and animal foods. However, plant protein and animal protein differ in composition, nutritional value and impact on health. Therefore, understanding their characteristics is crucial to choosing a protein source that suits you.
Characteristics Of Plant Protein And Animal Protein
(I) Plant protein
1. Source
Plant protein mainly comes from beans (such as soybeans, black beans, mung beans, etc.), cereals (such as wheat, rice, corn, etc.), nuts (such as almonds, walnuts, cashews, etc.) and seeds (such as sunflower seeds, pumpkin seeds, etc.).
2. Ingredients
Plant protein is usually rich in dietary fiber, vitamins and minerals, and has a low fat content, especially low saturated fat. Different plant protein sources have different amino acid compositions, but generally speaking, plant protein lacks certain essential amino acids, such as lysine and methionine.
3. Digestion And Absorption
The digestion and absorption rate of plant protein is relatively low, mainly because there are some anti-nutritional factors in plant protein, such as phytic acid, trypsin inhibitors, etc., which affect the digestion and absorption of protein. However, through processing (such as soaking, germination, fermentation, etc.), the content of anti-nutritional factors can be reduced and the digestion and absorption rate of plant protein can be improved.
(II) Animal Protein
1. Source
Animal protein mainly comes from meat (such as beef, pork, chicken, etc.), fish, eggs, milk, etc.
2. Ingredients
Animal protein contains all essential amino acids, and its amino acid composition is close to that of the human body, so it is considered to be high-quality protein. Animal protein is also rich in nutrients such as vitamin B12, iron, and zinc, but it also contains high fat and cholesterol, especially saturated fat and cholesterol.
3. Digestion And Absorption
The digestion and absorption rate of animal protein is relatively high, because the structure of animal protein is similar to that of human protein and is easily digested and absorbed by the human body.
The Impact Of Plant Protein And Animal Protein On Health
(I) Impact On Cardiovascular Health
1. Plant Protein
Studies have shown that consuming foods rich in plant protein can reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. Nutrients such as dietary fiber, vitamins and minerals in plant protein help lower blood pressure, blood lipids and blood sugar, and reduce the occurrence of atherosclerosis. In addition, the high content of unsaturated fat and low content of saturated fat in plant protein also helps protect cardiovascular health.
2. Animal Protein
Excessive intake of animal protein, especially red meat and processed meat, increases the risk of cardiovascular disease. This is because the high content of saturated fat and cholesterol in animal protein can lead to problems such as increased blood lipids and atherosclerosis. However, moderate intake of animal protein such as lean meat, fish, eggs and milk is beneficial to cardiovascular health.
(II) Impact On Kidney Health
1. Plant Protein
For people with normal kidney function, it is safe to consume a moderate amount of plant protein. However, for patients with kidney disease, due to the high content of non-high-quality protein in plant protein, it may increase the burden on the kidneys, so the intake of plant protein needs to be limited.
2. Animal Protein
Animal protein has a high content of high-quality protein. For people with normal kidney function, a moderate intake of animal protein can meet the needs of the body. However, for patients with kidney disease, excessive intake of animal protein may increase the burden on the kidneys, so it is necessary to properly control the intake of animal protein according to the condition.
(III) Impact On Weight Management
1. Plant Protein
Plant protein has a low fat content, especially low saturated fat content, and is rich in dietary fiber. These characteristics help control weight. Studies have shown that consuming foods rich in plant protein can increase satiety and reduce appetite, thereby helping to control weight.
2. Animal Protein
Animal protein has a high fat content, especially high saturated fat content. Excessive intake of animal protein may cause weight gain. However, a moderate intake of animal protein such as lean meat, fish, eggs and milk is necessary to maintain normal metabolism and muscle mass in the body.
Protein Sources Suitable For Different Groups Of People
(I) General Population
For the general population, both plant protein and animal protein are important sources of protein. It is recommended to maintain a balanced diet and consume a variety of protein foods in moderation, including beans, cereals, nuts, seeds, meat, fish, eggs and milk. This can ensure adequate intake of high-quality protein while also obtaining the benefits of other nutrients.
(II) Vegetarians
Since vegetarians do not consume animal protein, they need to pay more attention to the source and amount of protein intake. Vegetarians can meet their body's protein needs by consuming plant protein foods such as beans, cereals, nuts and seeds. In addition, vegetarians can also choose some protein supplements, such as soy protein, pea protein, etc., to ensure adequate intake of high-quality protein.
(III) Patients With Cardiovascular Disease
Patients with cardiovascular disease should reduce their intake of animal protein, especially red meat and processed meat. You can choose some foods rich in plant protein, such as beans, cereals, nuts and seeds, and at the same time consume animal protein such as lean meat, fish, eggs and milk in moderation. In addition, patients with cardiovascular disease should also pay attention to controlling the intake of total fat and cholesterol and increasing the intake of dietary fiber to protect cardiovascular health.
(IV) Patients With Kidney Disease
Patients with kidney disease need to appropriately control their protein intake according to their condition. For patients with severely impaired kidney function, it may be necessary to limit the intake of plant protein and animal protein to reduce the burden on the kidneys. When choosing protein foods, you should choose some foods with high quality protein content and low non-quality protein content, such as lean meat, fish, eggs and milk. At the same time, patients with kidney disease should also pay attention to controlling the total protein intake and avoid excessive protein intake.
Therefore, both plant protein and animal protein are important sources of protein, and they differ in nutritional value, digestion and absorption, and impact on health. For the general population, a balanced diet should be maintained and various protein foods should be consumed in moderation. For special groups such as vegetarians, patients with cardiovascular disease and patients with kidney disease, appropriate protein sources and intake should be selected according to their own conditions. When choosing protein foods, attention should be paid to the quality and diversity of the food, and the intake of other nutrients should be combined to maintain the health of the body.
As A Special Group Of People, How Should I Buy Plant Protein?
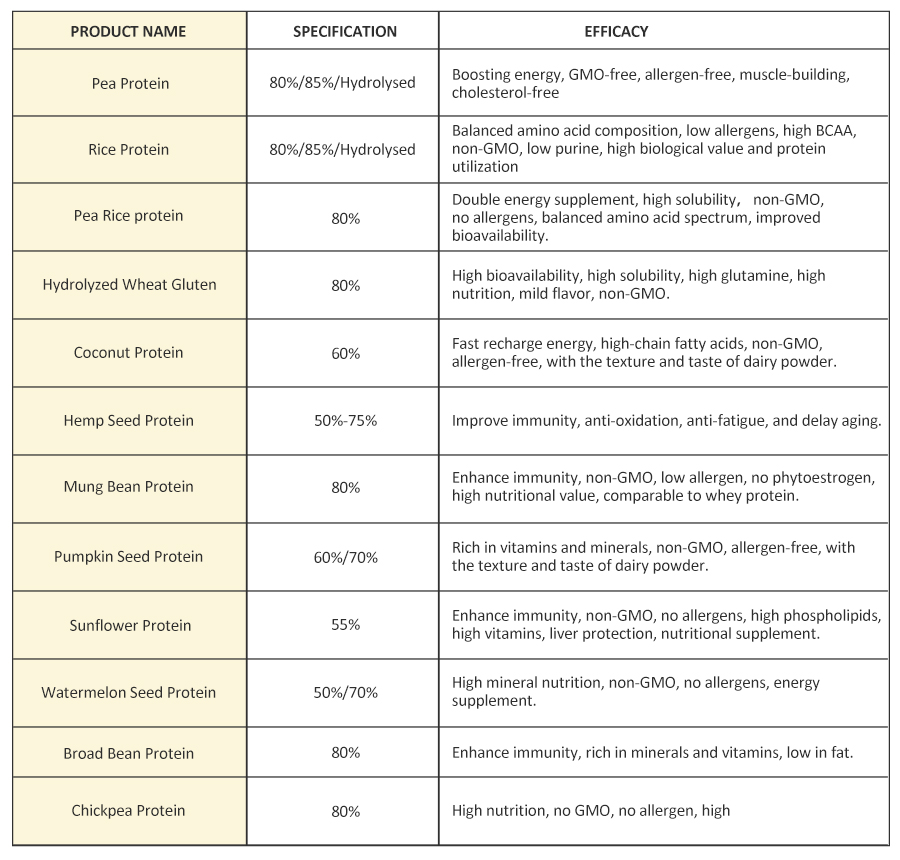
Recommend AMULYN Plant Based Protein Series for you:
Get Quotes
 Koicha Ceremonial Grade Matcha Powder
Koicha Ceremonial Grade Matcha Powder Organic Ceremonial Grade Matcha Powder
Organic Ceremonial Grade Matcha Powder Premium Beverage Grade Matcha Powder
Premium Beverage Grade Matcha Powder Everyday Culinary Grade Matcha Powder
Everyday Culinary Grade Matcha Powder Organic Instant Pure Matcha
Organic Instant Pure Matcha Soy Lecithin Powder
Soy Lecithin Powder Sunflower Lecithin Powder
Sunflower Lecithin Powder Soy Lecithin Granules
Soy Lecithin Granules Phosphatidylcholine
Phosphatidylcholine  Phosphatidylserine
Phosphatidylserine Soy Lecithin Liquid
Soy Lecithin Liquid Reishi Mushroom Powder
Reishi Mushroom Powder Lion's Mane Mushroom Powder
Lion's Mane Mushroom Powder Cordyceps Sinensis Powder
Cordyceps Sinensis Powder Chaga Mushroom Powder
Chaga Mushroom Powder Shiitake Mushroom Powder
Shiitake Mushroom Powder Cordyceps Militaris Powder
Cordyceps Militaris Powder



























































